
What's the difference between hydrophobic membrane filters and hydrophilic membrane filters?
Hydrophobic membrane filters don't have an affinity for water, and they're ideal for applications such as venting. On the other hand, hydrophilic membrane filters have an affinity for water, and you can use them with almost any kind of liquid.
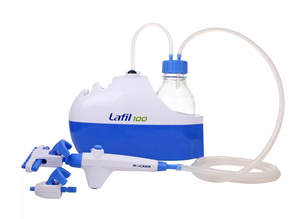
Vacuum filtration is a laboratory procedure that utilizes an oil-free vacuum pump, filter apparatus, filter flask, and often a filtration manifold to perform membrane filtration protocols.

When it comes to purchasing tools and equipment in a laboratory, one requires careful consideration. Most tools in a lab are used over a long period. Therefore, it is important to purchase the right tool for the job that can stay durable.

Thermal cyclers come to mind while thinking of DNA/RNA analysis in molecular biology. Thermal cyclers (also known as PCR machines or thermocyclers) are scientific instruments for replicating, analyzing, detecting, and amplifying DNA or RNA segments.

While there are plenty of ways to mix chemicals in your lab, nothing beats the power and precision of a laboratory shaker when you need to mix solutions thoroughly and efficiently.

So you’re looking for a hotplate or stirrer. The choices are bewildering. We admit, we’ve got a remarkable variety in what we offer. That can be confusing. If you get in touch with us about your needs, we’re happy to help you refine your search. If you’re just starting out, let’s give you some basic counsel here. What are the things you should think about as you consider your needs and the various options?

Health authorities are hamstrung here, because of a paucity of data. We still know far less about COVID viruses in general, and COVID-19 in particular, than we’d like. We know about how far they can travel, person to person, about how long they can survive on various surfaces and in the air, and we know sort of how they replicate. But we don’t know anything about their ability to confer immunity, or why they hit some parts of the population harder than others.

Sample prepping gets better all the time – cleaner, faster, and cheaper. One of the reasons for better speed and cleaner sampling is the arrival of disposable polypropylene pipette tips, that you throw away after a single use. These really lower processing time, and they do away with any fear of cross-contamination. One of the old bottlenecks in laboratory processing is solid-phase extraction. It’s entirely possible to use disposable tips for this too.

One of our popular products here at Next Day is the Cryo-Safe™ freeze controller from Bel Art. It’s a well-engineered piece of equipment. It absolutely assures a drop in cell temperature of 1°C per minute, and a lot of labs want that, at high precision.
But where does that 1°C gradient rule come from? And is it right for every possible application?
It’s a fair question, and not every person in every lab is always clear about this. So here’s an answer, first in the form of a review of the general challenges in cryopreservation, and then a bit of discussion about cooling rates, and how they’re derived.

The premium workmanship of the robust die-cast aluminum housing, coupled with the finest engineering materials and design, provides excellent protection against mechanical and electrical interference. This allows the balance to operate at the highest levels of precision, from the initial weigh-in period through the final result. With features such as self-calibration system and the intuitive user settable operation, the balance will handle any task you set for it. For more information, review the specifications of the individual balances.

The first centrifuge was built by Alexander Prandtl in 1875 as a mean of separating cream from milk. Since then, the laboratory centrifuge developed to be a principal tool in scientific and clinical labs.
The Centrifugation concept and applications:
When an object is put in rotation around an axis, an outward radial force is applied on it. This centripetal force is used to accelerate Sedimentation, a process where denser particles move faster to the bottom, or in a centrifuge, towards an outward direction. This principle is used for several different applications in the modern lab, with the purpose of separating different constitutes within a solution:

The first step is to choose the right sized filter paper, which is the most vital step for vacuum filtration, because the filter must be smaller in diameter than the Hirsch or Buchner funnel. It needs to cover the holes and sit flat on the funnel bottom and not have any creases or folds. There are two ways to fold the filter paper, which are the fluted and conventional methods.
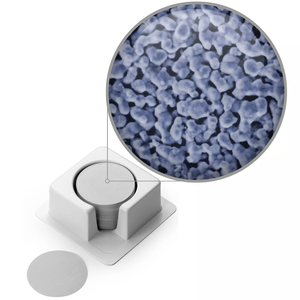
Membrane filtration utilizes pressure in order to force water or any other kind of carrier fluid through a porous or semi-permeable membrane. This process separates the particulate matter that's suspended from the soluble and fluid components.
Membrane filters are also known as membranes are microporous films which have specific ratings for their pore sizes. These are also known as microporous filters, screens or sieves, and they keep the microorganisms or particles which are bigger than the size of their pores through the process of surface capture. On the other hand, any particles smaller than the pore size of the membrane filter are typically kept by other types of mechanisms.

